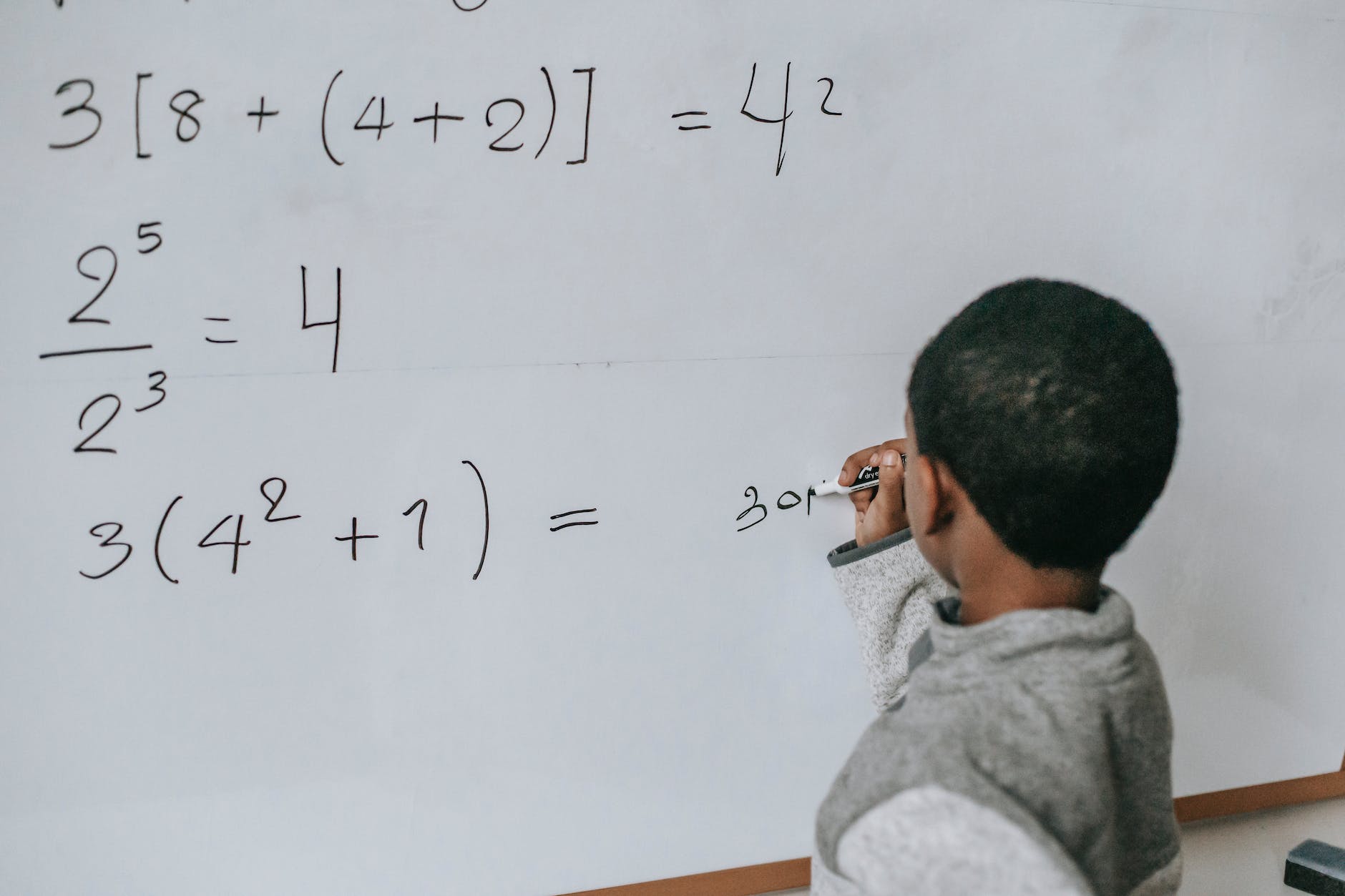
A quick review of P.E.M.D.A.S. (PEMDAS) reminds us that it is an acronym for the order of operations rules. Namely, Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction. This time, we will take a deeper look at the third problem on the board. It contains Exponents, Parentheses (Multiplication) and Addition.
Identification
We start with identification of the terms:
- Addition: 42+1
- Exponent: Exponent – 42
- Parentheses (Multiplication): 3(E+A)
This problem uses terms including Exponents, Addition and Parentheses. An Exponent is the number of times a number, called a coefficient, is multiplied by itself. the coefficient in this problem is 4. This problem uses PEMA but must be solved in this order EAPM.
Concept
The concept states, Parentheses must be solved first; however because the Exponent and Addition are Inside the Parentheses, the Exponent must be solved before the Addition.
Solution
It is as simple as:
First, the Exponent must be solved – 42 =(4X4)=16. Next the Addition 16+1=17. Finally, the Parentheses/Multiplication can be solved: 3(17)=51.
Summary
In summary, following PEMDAS guides how problems are solved in a uniform process. This problem asks a student to recognize why the Exponent inside the Parentheses takes priority over the Parentheses/Multiplication, therefore, it is also an exercise in pattern recognition. Mental math resources for the Addition and Multiplication will make the calculations faster and the patterns easier to see. Students who have solid mental math skills are more confident and able to understand concepts better. If your student takes the time to build or re-build an unstable mental math foundation, It is the best and fastest way to concept comprehension. Contact me – I CAN help. Until next time. dream BIG and let your D.R.E.A.M.S. take you there!